To crystallize these concepts rather than build another new computer, Raskin instead began work on a software package with a team that included his son AZA, initially called HumaneEditor. The HumaneEditor project was first revealed to the world on Christmas Eve 2002, although initially only as a source code CVS tree because it was considered very unfinished. Early versions of the HumaneEditor were open source and were designed to run on classic Mac OS 9, although Qemu, Sheepshaver, and Classic under Tiger and earlier will also run on it.
Default document.
Credit: Cameron Kaiser
As before, the human editor uses a large central workspace divided into individual documents, here separated by backslashes. Our familiar two-tone cursor is also retained. However, while font sizes, bold, italics and underlines were supported, colors (and by extension, font sizes) were still selected via traditional MAC drop-down menus.
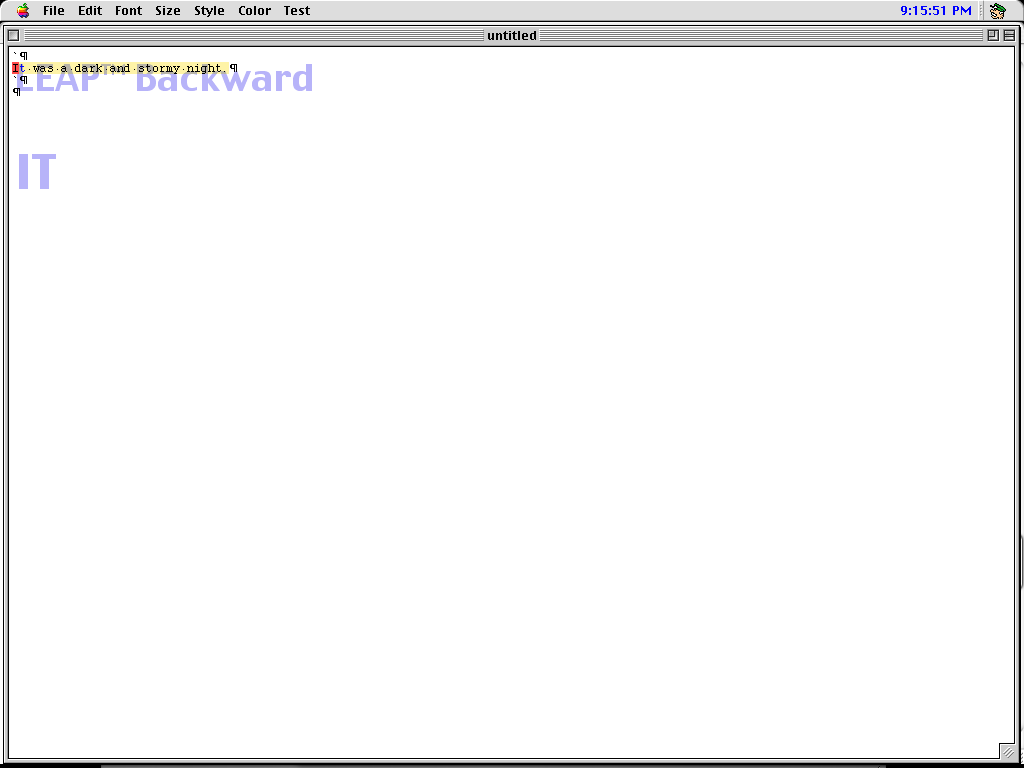
Jump with the shift and angle bracket keys.
Credit: Cameron Kaiser
The jump, here with the trademark, is back front and center. However, rather than being a special key, the jump is just part of an internal command line called a humanoid quasi-mode where other commands can be sent. Notice that the prompt is displayed as transparent text in the work area.
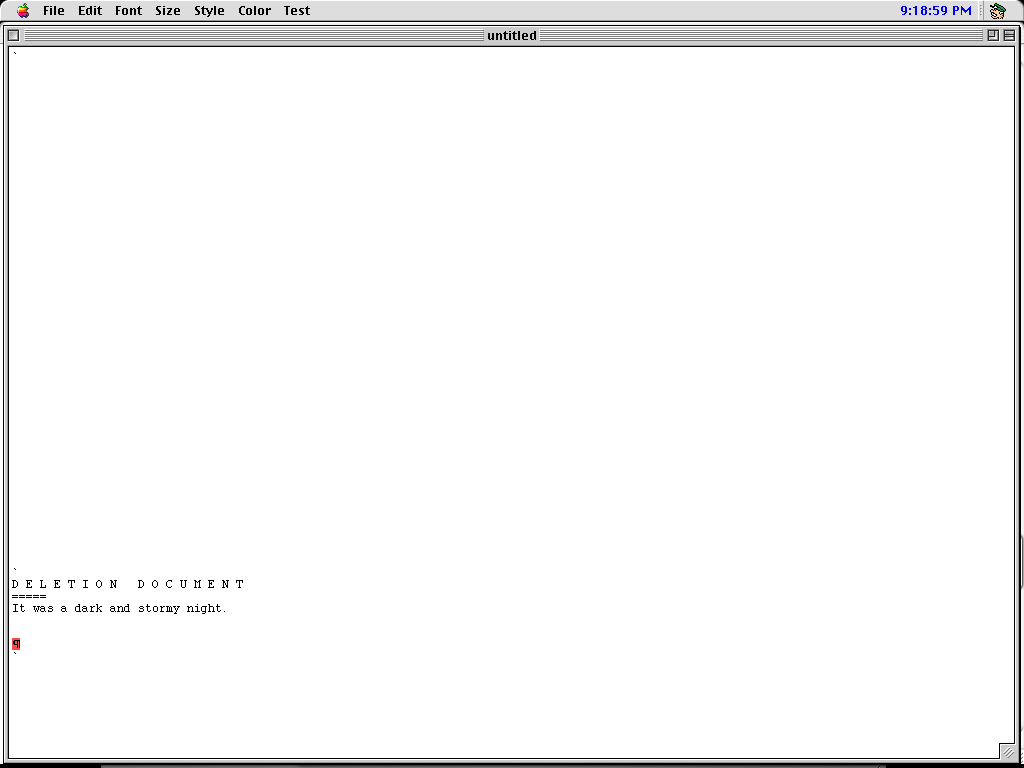
Deletion document.
Credit: Cameron Kaiser
When text was deleted, either by backspace or by pressing delete with a region selected, a “delete document” was automatically created and maintained from which it could be saved. In effect, this turned the workspace into a yank buffer with all your documents, and thus undoing any destructive editing operation became just another cut and paste. (Delete from the delete document that you just deleted.)
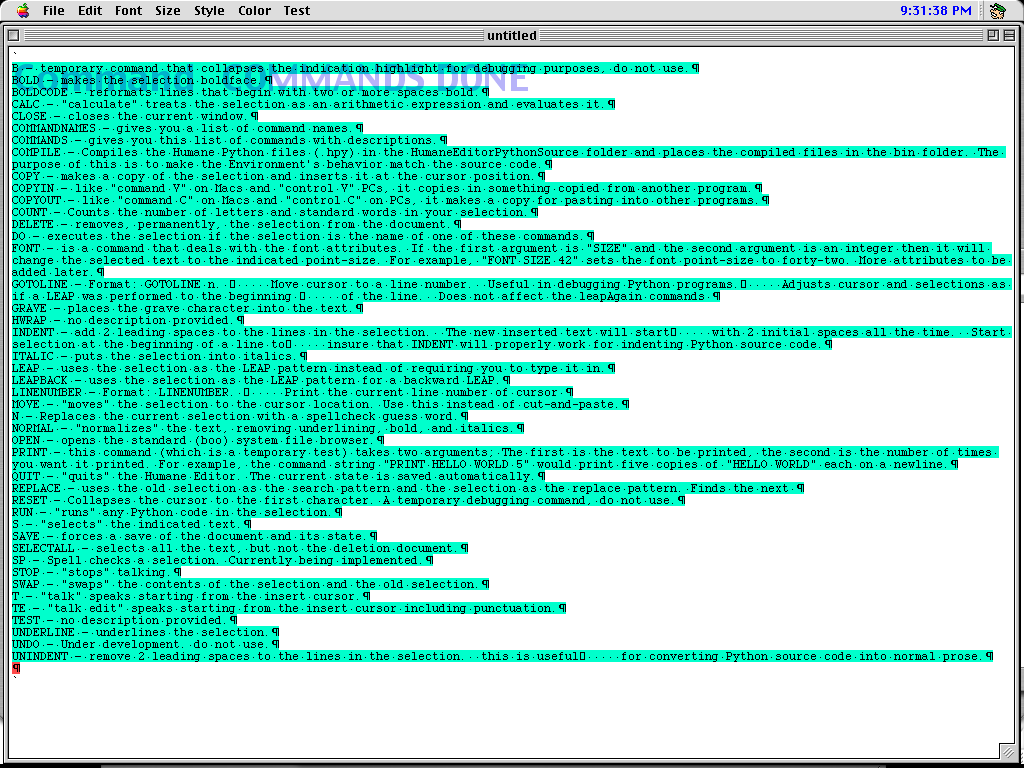
List of commands.
Credit: Cameron Kaiser
The full list of commands accepted by Quasimode was available by typing commands, which in turn emitted them into the document. These are based on pre-compiled Python files that the user could edit or add to, and arbitrary Python expressions and code could also be inserted and run directly from the document’s workspace.















